Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14(TNFRSF14) ELISA kit
-
中文名称:人肿瘤坏死因子配体超家族成员14(TNFSF14)酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:CSB-EL023973HU
-
规格:96T/48T
-
价格:¥3600/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:人肿瘤坏死因子配体超家族成员14(TNFSF14)是免疫调节的关键分子,通过参与淋巴细胞活化、炎症反应及血管生成等过程,在肿瘤微环境调控和自身免疫性疾病中发挥重要作用。本试剂盒(货号CSB-EL023973HU)采用双抗体夹心法原理实现定量检测,支持对血清、血浆及组织匀浆样本中TNFSF14蛋白的精准分析,检测灵敏度覆盖15.6-1000 pg/mL的宽线性范围。其高特异性抗体组合可有效排除样本基质干扰,适用于细胞因子网络研究、肿瘤免疫微环境分析及炎症性疾病机制探索等科研领域,例如在动物模型或体外实验中评估TNFSF14表达水平与疾病进展的关联性,或作为免疫治疗相关基础研究的定量工具。该产品严格遵循质量控制标准,可为科研工作者提供稳定可靠的实验数据支持。
-
别名:HVEML ELISA Kit; ATAR ELISA Kit; CD270 ELISA Kit; CD40 like protein precursor ELISA Kit; Herpes virus entry mediator A ELISA Kit; Herpesvirus entry mediator A ELISA Kit; Herpesvirus entry mediator ELISA Kit; Herpesvirus entry mediator ligand ELISA Kit; HveA ELISA Kit; HVEM ELISA Kit; HVEM L ELISA Kit; LIGHT ELISA Kit; LIGHTR ELISA Kit; TNFRSF14 ELISA Kit; TNFSF 14 ELISA Kit; TNR14_HUMAN ELISA Kit; TR2 ELISA Kit; Tumor necrosis factor receptor like gene2 ELISA Kit; Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 ELISA Kit; Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 precursor ELISA Kit; Tumor necrosis factor receptor-like 2 ELISA Kit
-
缩写:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
样本类型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates
-
检测范围:15.6 pg/mL-1000 pg/mL
-
灵敏度:3.9 pg/mL
-
反应时间:1-5h
-
样本体积:50-100ul
-
检测波长:450 nm
-
研究领域:Immunology
-
测定原理:quantitative
-
测定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8%
Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess.
Intra-Assay Precision
Inter-Assay Precision
Sample
1
2
3
1
2
3
n
20
20
20
20
20
20
Mean(pg/ml)
133.445
127.689
126.259
121.987
125.188
124.119
SD
0.029
0.025
0.023
0.035
0.039
0.034
CV(%)
5.206
4.621
4.283
6.667
7.303
6.403
-
线性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of human TNFRSF14 in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay.
Sample
Serum(n=4)
1:1
Average %
88
Range %
85-99
1:2
Average %
95
Range %
89-103
1:4
Average %
93
Range %
89-101
1:8
Average %
90
Range %
85-98
-
回收率:
The recovery of human TNFRSF14 spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section.
Sample Type
Average % Recovery
Range
Serum (n=5)
89
83-95
EDTA plasma (n=4)
93
85-101
-
标准曲线:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed.
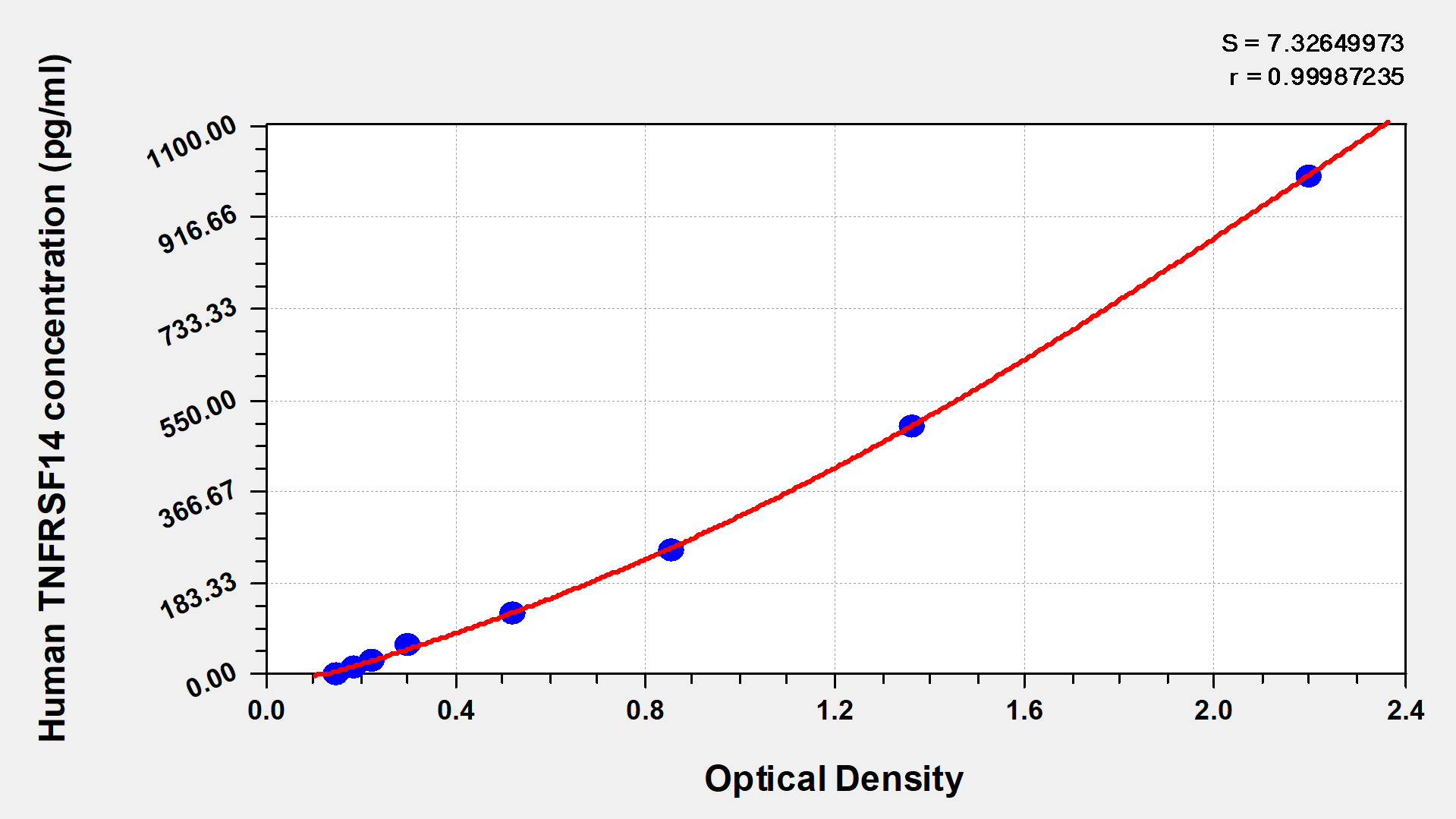
pg/ml
OD1
OD2
Average
Corrected
1000
2.243
2.148
2.196
2.030
500
1.379
1.352
1.366
1.200
250
0.824
0.904
0.864
0.698
125
0.522
0.547
0.535
0.369
62.5
0.309
0.316
0.313
0.147
31.2
0.247
0.232
0.240
0.074
15.6
0.198
0.201
0.200
0.034
0
0.166
0.165
0.166
-
数据处理:
-
货期:3-5 working days
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Receptor for four distinct ligands: The TNF superfamily members TNFSF14/LIGHT and homotrimeric LTA/lymphotoxin-alpha and the immunoglobulin superfamily members BTLA and CD160, altogether defining a complex stimulatory and inhibitory signaling network. Signals via the TRAF2-TRAF3 E3 ligase pathway to promote immune cell survival and differentiation. Participates in bidirectional cell-cell contact signaling between antigen presenting cells and lymphocytes. In response to ligation of TNFSF14/LIGHT, delivers costimulatory signals to T cells, promoting cell proliferation and effector functions. Interacts with CD160 on NK cells, enhancing IFNG production and anti-tumor immune response. In the context of bacterial infection, acts as a signaling receptor on epithelial cells for CD160 from intraepithelial lymphocytes, triggering the production of antimicrobial proteins and proinflammatory cytokines. Upon binding to CD160 on activated CD4+ T cells, downregulates CD28 costimulatory signaling, restricting memory and alloantigen-specific immune response. May interact in cis (on the same cell) or in trans (on other cells) with BTLA. In cis interactions, appears to play an immune regulatory role inhibiting in trans interactions in naive T cells to maintain a resting state. In trans interactions, can predominate during adaptive immune response to provide survival signals to effector T cells.; (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Herpes simplex virus 1/HHV-1.; (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Herpes simplex virus 2/HHV-2.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Data suggest that both HVEM and UL144 bind a common epitope of BTLA, whether engaged in trans or in cis; these studies were conducted in cell lines representing B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, and natural killer cells. (HVEM = human herpes virus entry mediator; UL144 = membrane glycoprotein UL144 of Human herpesvirus 5; BTLA = human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator) PMID: 29061848
- our data suggested that the BTLA/HVEM pathway contributes to peripheral T cell suppression in hepatocellular carcinoma patients PMID: 30116751
- TNFRSF14 may serve a tumor suppressive role in bladder cancer by inducing apoptosis and suppressing proliferation, and act as a novel prognostic biomarker for bladder cancer. PMID: 30066919
- Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphomas with concomitant 1p36 deletion and TNFRSF14 mutations frequently express high levels of EZH2 protein. PMID: 29858685
- High HVEM Expression is Associated with Cancer Progression in Breast Cancer. PMID: 28612127
- Report a variant of t(14;18) negative nodal diffuse follicular lymphoma with CD23 expression, 1p36/TNFRSF14 abnormalities, and STAT6 mutations. PMID: 26965583
- Roles of HVEM are likely to be immunosuppressive rather than activating tumor immunity and it in peripheral blood is a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. PMID: 27987232
- Low HVEM expression is associated with pancreatic and ampullary cancer. PMID: 28470686
- HIV-1 produced from CD4+ T cells bears HSV-2 receptor HVEM and can bind to and enter HSV-2-infected epithelial cells depending on HVEM-gD interaction and the presence of gB/gH/gL. PMID: 28809154
- Transgenic mice expressing HVEMIg showed a complete resistance to the lethal infection even with 300 MLD50 (survival rate of 100 %). PMID: 28671524
- HVEM is highly expressed in ovarian serous adenocarcinoma tissues and correlated with the patient clinicopathological features. PMID: 28365939
- TNFRSF14 and MAP2K1 mutations are the most frequent genetic alterations found in pediatric-type follicular lymphoma (PTFL) and occur independently in most cases, suggesting that both mutations might play an important role in PTFL lymphomagenesis. PMID: 28533310
- genetic landscape of Pediatric-type follicular lymphoma suggests that TNFRSF14 mutations accompanied by copy-number neutral loss of heterozygosity of the 1p36 locus in over 70% of mutated cases, as additional selection mechanism, might play a key role in the pathogenesis of this disease. PMID: 27257180
- The increased immune-stimulatory capacity of lymphoma B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations had clinical relevance, associating with higher incidence of acute GVHD in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. PMID: 27103745
- These results suggest that TNFRSF14 mutations point towards a diagnosis of follicular lymphomas , and can be used in the sometimes difficult distinction between marginal zone lymphomas and follicular lymphomas PMID: 27297871
- the overexpression of HVEM in ovarian cancer cells may suppress the proliferation and immune function of T cells, thus leading to the development of ovarian cancer. The current study partially explains the immune escape mechanism of ovarian cancer cells. PMID: 27458100
- In eight cases (42%) we observed recurrent copy number loss of chr1:2,352,236-4,574,271, a region containing the candidate tumor suppressor TNFRSF14. PMID: 26650888
- Study report the crystal structure of unbound HVEM, which further contributes to the understanding of the molecular mechanisms controlling recognition between HVEM and its ligands. PMID: 26202493
- HVEM may play a critical role in tumor progression and immune evasion PMID: 25750286
- Data indicate that tumour-expressing herpes virus entry mediator (HVEMplays a critical role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), suggesting targeting HVEM may be a promising therapeutic strategy for HCC. PMID: 25468715
- Relative expression of HVEM and LTbetaR modulates canonical NF-kappaB and pro-apoptotic signals stimulated by LIGHT. PMID: 24980868
- Sequencing of TNFRSF14 located in the minimal region of loss in 1p36.32 showed nine mutations in pediatric follicular lymphoma. PMID: 23445872
- HVEM plays a critical role in both tumor progression and the evasion of host antitumor immune responses, possibly through direct and indirect mechanisms. PMID: 24249528
- HVEM gene polymorphisms are associated with sporadic breast cancer in Chinese women. PMID: 23976978
- The conformation of the N-terminus of herpes simplex virus gD is induced by direct binding to HVEM and nectin-1. PMID: 24314649
- HVEM functions as a regulator of immune function that activates NK cells via CD160 and limits lymphocyte-induced inflammation via association with B and T lymphocyte attenuator PMID: 23761635
- BTLA and HVEM may have roles in graft rejection after kidney transplantation PMID: 23375291
- Studies indicate co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory receptors B7-1, B7-2, CD28 and TNFRSF14 have a pivotal role in T cell biology, as they determine the functional outcome of T cell receptor (TCR) signalling. PMID: 23470321
- These findings support role for BTLA and/or HVEM as potential, novel diagnostic markers of innate immune response/status and as therapeutic targets of sepsis. PMID: 22459947
- study described the expression and spatial distribution of HVEM and BTLA in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissues, and results indicated that HVEM/BTLA may be involved in regulating the progress of joint inflammation PMID: 22179929
- HVEM-B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) interactions impair minor histocompatibility antigen (MiHA)-specific T cell functionality, providing a rationale for interfering with BTLA signaling in post-stem cell transplantation. PMID: 22634623
- Results indicate that mHVEM on leukocytes and sHVEM in sera may contribute to the development and/or progression of gastric cancer. PMID: 22113134
- These results suggest that the C-terminal portion of the soluble HVEM ectodomain inhibits herpes simplex virus type 1 gD activation and that this effect is neutralized in the full-length form of HVEM in normal infection. PMID: 22239829
- TNFRSF14 appears to be a serious candidate gene that might contribute to follicular lymphoma development. PMID: 21941365
- HVEM-BTLA cis complex provides intrinsic regulation in T cells serving as an interference mechanism silencing signals coming from the microenvironment. PMID: 21920726
- The results of a mutagenesis study of HVEM suggest that the CD160 binding region on HVEM was slightly different from, but overlapped with, the BTLA binding site. PMID: 21959263
- data show that HVEM stimulatory signals promote experimental colitis driven by innate or adaptive immune cells PMID: 21533159
- Polymorphisms were associated with MS predisposition, with stronger effect in patients with HHV6 active replication-TNFRSF6B-rs4809330(*)A: P=0.028, OR=1.13; TNFRSF14-rs6684865(*)A: overall P=0.0008, OR=1.2. PMID: 20962851
- Findings identify TNFRSF14 as a candidate gene associated with a subset of FL, based on frequent occurrence of acquired mutations and their correlation with inferior clinical outcomes. PMID: 20884631
- We have identified and replicated a novel gene-gene interaction between 2 polymorphisms of TNFRSF members in Spanish patients with RA, based on the hypothesis of shared pathogenic pathways in complex diseases. PMID: 20187130
- Results provide evidence of an existing relationship between HVEM and obesity, which suggest that this TNF superfamily receptor could be involved in the pathogenesis of obesity and inflammation-related activity. PMID: 19680232
- Data suggest involvement of TNF superfamily receptor members and ligands in human atherosclerosis. TNFRSF14 (HVEM, TR2, LIGHTR)analysis, found this receptor in regions rich in CD68-positive macrophage-derived foam cells and HLA-DR-positive cells. PMID: 11742858
- Crystallization and preliminary diffraction studies of the ectodomain of the envelope glycoprotein D from herpes simplex virus 1 alone and in complex with the ectodomain of the human receptor HveA PMID: 11976496
- association of HVEM and nectin-1 with lipid rafts during herpes simplex virus entry PMID: 12915568
- sHVEM levels were elevated in sera of patients with allergic asthma, atopic dermatitis and rheumatoid arthritis PMID: 14749527
- both nectin 1 and HVEM receptors play a role during HSV infection in vivo and both are highly efficient even at low levels of expression PMID: 15110526
- Binding of HVEM to BTLA attenuates T cell activation, identifying HVEM/BTLA as a coinhibitory receptor pair. PMID: 15647361
- in cells a complex forms through physical associations of HVEM, HSV-1 gD, and at least gH PMID: 15767456
- distinct herpesviruses target the HVEM-BTLA cosignaling pathway, suggesting the importance of this pathway in regulating T cell activation during host defenses. PMID: 16131544
- 2.8-A crystal structure of the BTLA-HVEM complex shows that BTLA binds the N-terminal cysteine-rich domain of HVEM and employs a unique binding surface PMID: 16169851
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed, with the highest expression in lung, spleen and thymus. Expressed in a subpopulation of B cells and monocytes. Expressed in naive T cells.
-
数据库链接:



















